This guide provides a step-by-step process for installing Docker on AlmaLinux and CentOS VPS servers. Ensure you have SSH access and root level priviledges to your VPS before starting. The process involves updating the system, checking and installing necessary packages, adding Docker repositories, and verifying the installation. Follow these instructions carefully for a successful Docker setup.
Step 1: Update the System
Begin by updating your system. Once you have accessed your VPS via SSH, execute the command sudo yum update -y to ensure your system packages are up to date.
Step 2: Verify and Install Required Packages
After updating, verify the installation of the yum-utils package. Run sudo yum install yum-utils to check and install it if necessary. After confirming the package is installed, proceed to add the Docker repository.
Step 3: Add Docker Repository
To add the Docker repository, execute the command sudo yum-config-manager –add-repo along with the appropriate repository URL. Once added, proceed to install Docker’s CLI and container tools.
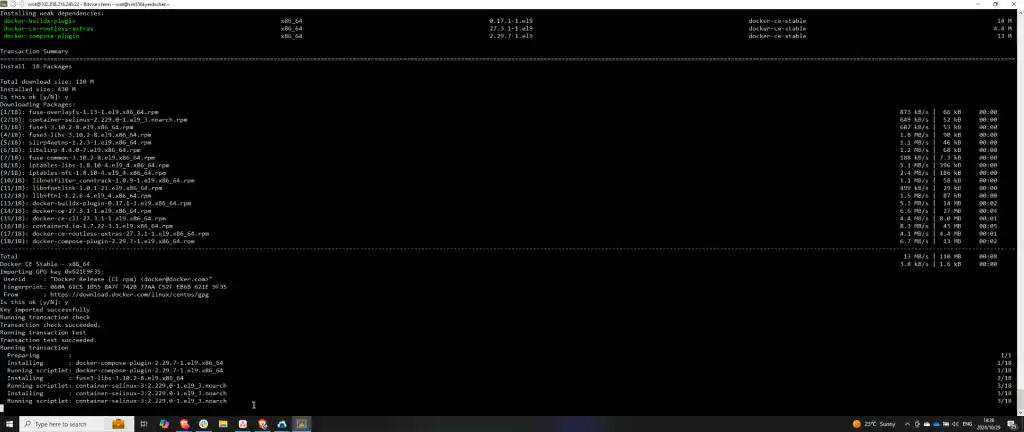
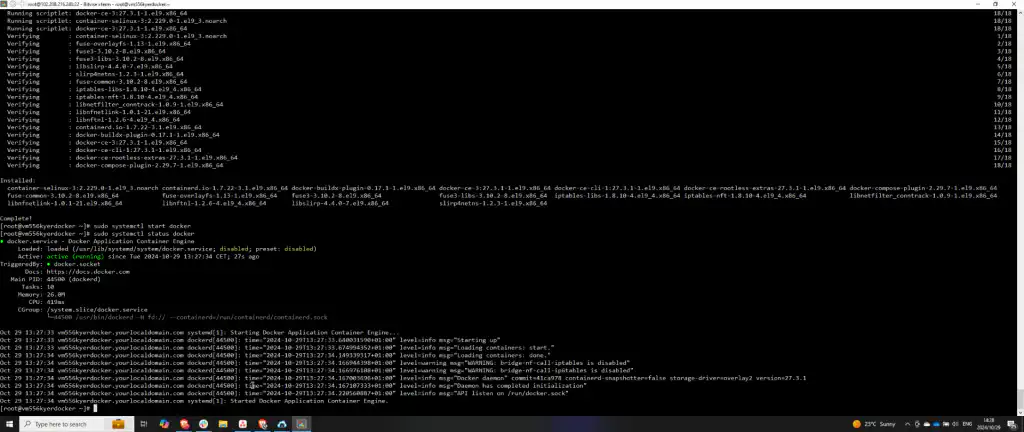
Step 4: Install and Start Docker
After installing the Docker container tools, start the Docker service by executing sudo systemctl start docker. Verify the service is running by checking its status with sudo systemctl status docker.
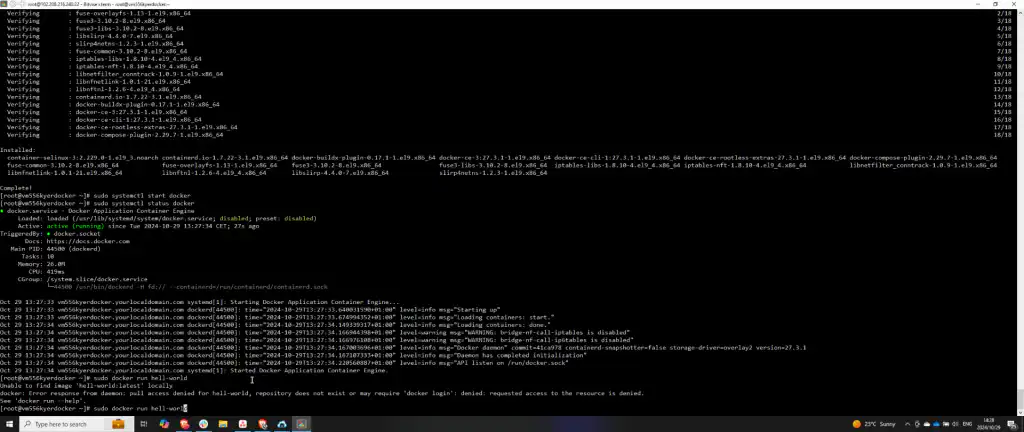
Step 5: Test Docker Installation
Once confirmed that Docker is active, test the installation by running a test container. Execute sudo docker run hello-world to ensure Docker is correctly set up and functioning.
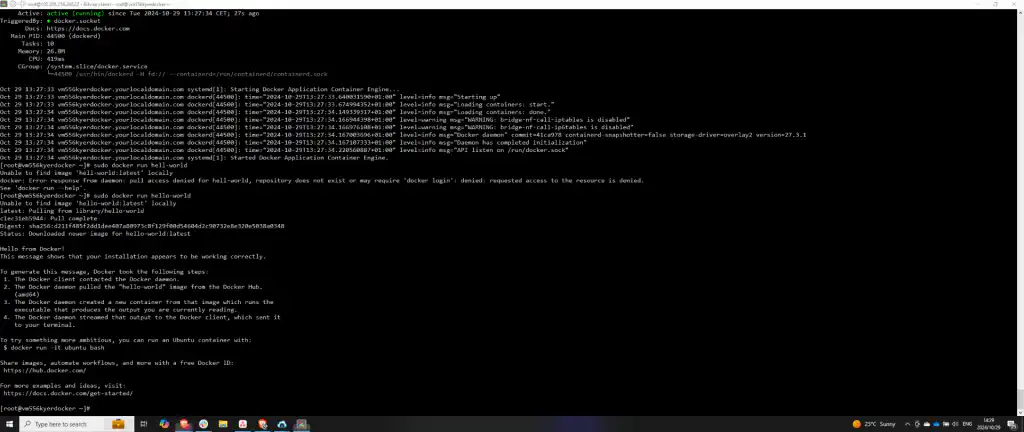
Step 6: Confirm Successful Setup
To further confirm Docker’s operation, run sudo docker run hello-world once more. This repetition ensures the Docker setup was successful and is operating correctly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do if the Docker service fails to start?
If the Docker service fails to start, first check the status with sudo systemctl status docker to view detailed error messages. Ensure that all dependencies are installed and compatible. If you encounter issues, try restarting the service using sudo systemctl restart docker and review the Docker logs with journalctl -u docker.
How do I add a specific version of Docker to my system?
To install a specific version, first, list all available versions using yum list docker-ce –showduplicates | sort -r. Then, you can install a chosen version by specifying it in the command, like sudo yum install docker-ce-<version> docker-ce-cli-<version>.
Can I use Docker without root privileges?
Yes, it is possible to use Docker without root privileges by adding your user to the Docker group. Execute sudo usermod -aG docker $USER and then log out and back in for the changes to take effect. This allows non-root users to run Docker commands.
How can I completely remove Docker from my system?
To remove Docker, use the command sudo yum remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io to uninstall the packages. Additionally, delete Docker directories like /var/lib/docker if you wish to clear all Docker-related data.